6.a.1. The theoretical basis for The EDI Study
The EDI Study, done in 2002, can be found in the corresponding book online. It analyzed more than 500 million coefficients of determination.
One of the main arguments to justify the Conditioned Evolution of Life –CEL– is the Logical Verification of Information, transmitted –LoVeInf. To contrast its existence, we must find a model with the following hypotheses:
Evolution with the method LoVeInf for the studied capacity
-
The existence of a function ξ (I) that measures the different potentials of the capacity.
We believe the cognitive ability represented by the IQ test fulfills both requisites of the model.
The possibility of verifying the CEL through the LoVeInf method, the Darwin-out and Menssalina experiments, or others makes the theory scientific.
Other reasons for choosing intelligence are that it is a very controversial topic and, if confirmed, shows a part of the CEL significant repercussions in the world of education.
There are numerous studies based on individual IQ –intelligence quotient– measurements. The research works have contradictory conclusions, whereas identical twins’ studies show 80-85% correlation, while for other types of kin relations, they decrease to 30%.
For us, the conclusion is that genetic inheritance is the leading cause of the evolution of intelligence, as the high correlation between identical twins demonstrates. The low correlation is due to the incorrect definition of the form the inheritance occurs according to the CEL.
In other words, the low correlations between the IQs of non-twin brothers are due to the Mendelian combination of chromosomes. The correlation between the flower or rat sisters' color in the typical examples of Mendel's laws would also obtain low values. We must bear in mind the difference between genetic and predetermined characteristics and their concordance.
The statistical model could not produce the expected results due to both the chosen variable's multifunctional nature and the possibility that the genetic code could be in various chromosomes, making the model’s design much more difficult.
Another possibility is the results showing a heritability of intelligence of 50% and simultaneously that the dominance rules are consistent with the CEL proposals, depending on the Logical Verification of Information –LoVeInf, the primary objective of the model.
The IQ refers to the relative position defined within a standardized function ξ (I) of the statistical distribution for its validation process.
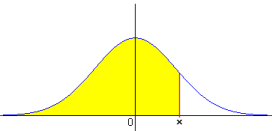
The figure shows the shape of the Normal function ξ (IQ) we will use. For each IQ value, the function indicates the accumulated probability that the population's IQ is the same or less than the IQ reference value.
For example, x (100) = 0.5 and the opposite function ξ-inv (Prob.) = IQ, that means, ξ-inv (0.5) = 100.
The function will link each one of its values with the accumulated percentile.
As its name indicates, the percentile is the percentage of the reference population with potential equal to or smaller than the referred distribution value. Thus, the percentile of value 100 of these distributions is 0.50 or 50%, as the mean of the Normal distribution is 100.
Wechsler, Stanford-Binet, and Cattell scales are the most used. They all use a Normal function of an average of 100. However, they differ in the standard deviation: 15, 16, and 24, respectively.
We will use the following case to formalize our model of intelligence evolution. Although many more possibilities may exist, the following reasoning or similar will apply to all of them.
Combining the four chromosomes in agreement with Mendelian genetic significance and the LoVeInf method will produce the four different outcomes shown in the figure. The expected mathematical average of the new individual's capacity will be the sum of each case weighed by its probability.
EC descendant = P(D1) C(D1) + P(D2) C(D2) + P(D3) C(D3) + P(D4) C(D4)
The probabilities of all of them will be equal to 0.25. The LoVeInf assumption implies that the significant chromosome will be the one with less capacity. At the most, it would only be possible to express that gene's potential in his integrity.
We will suppose for simplification that the smaller gene's cognitive ability entirely expresses since, for a specific capacity, the more significant chromosome contains practically all the trimmer's information.
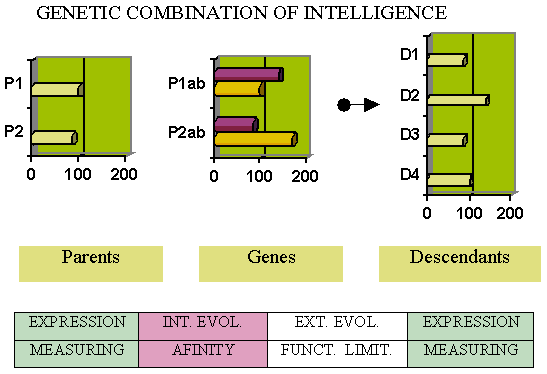
As the significant gene will be the less potent, the IQ tests cannot measure each parent's more powerful genetic information with current technology since it does not manifest in its entirety.
Therefore, it will be necessary to estimate the second and third adding, limiting as far as possible, the values of C (D2) and C (D4.) If we always worked with probabilities of its mathematical expected average, the errors would compensate when calculating the correlation between dependent and independent variables.
Even if we could measure the most potent chromosome, the randomness of the Mendelian inheritance would remain.
P1a and P2b chromosomes are present in D2, while P1b and P2b are present in D4. Among these three chromosomes, we only know the potential of P1b is 100. Thus, to estimate D2 and D4 (ED2 and ED4) potential, we need to previously assess P1a and P2b (EP1a and EP2b.)
We can reduce EP2b to its expected mean, this is, the average IQ values above P2a. Being the potential related to percentile (ξ-inv) the inverse function, we will obtain the following equation:
EP2b = ξ-inv [ξ (P2a) + (1 - ξ (P2a) / 2)]
The intermediate value estimates are not very accurate when measured individually. However, the aim is to obtain unbiased estimates given that, due to the effect of the Mendelian-chromosome combination, the deviations’ variance will always be very high.
The experiment’s positive outcome could show the intelligence evolution is mostly due to genetic inheritance, and it follows the LoVeInf rules.
Once the empirical research's IQ data is available, it will be possible to analyze the correlation between the model's explanatory variables with the explained ones.
Fortunately, the book online of The EDI Study (2002) presents the results confirming the proposals of the scientific theory of CEL, r² = 0.96 and higher.
Regardless of the definition of intelligence in evolutionary psychology as a group of relational functions, there are some simplifications to ease the CEL model. To make estimations of the evolution of intelligence more coherent, surely it could be necessary to include:
The internal improvement of the genetic information in each generation could exceed 10% regarding intelligence evolution.
The affinity filter relates to the lack of full expression of the smaller intellectual power, as mentioned above.
-
Another factor could be the effect of the sexual selection associated with the correlation of the intellectual power between progenitors’ chromosomes.
It is possible to make a preliminary sensitivity analysis for the estimation of the previous parameters.
Afterward, The EDI Study confirmed the three aspects mentioned above.
6.a.2. Research on the evolution of memory and other cognitive functions
The hypothesis of Logical Verification of the Information –LoVeInf– received can be negatively or contrary to the one assumed for intelligence evolution. It would lead to a reformulation of the model to contrast.
Both assumptions are part of the same theory of evolution and occur for different capacities.
Oxford scientists discover a gene that affects explicitly language.
A mutation of the gene, they have named FOXP2. The correlation is perfect: the 15 affected family members carry the mutated gene, and the other 14 carry the normal gene.
The mutation does not function using a breakage spread by intelligence since many affected have ordinary intellectual (non-verbal) levels. Some have intellectual levels that are greater than their non-affected family members are.
El País 04-10-2001. Nature
For reliable or mathematical memory, the hypothesis will be the same as intelligence; it will be the contrary for standard memory and intuition.
The issue gets complicated with other cognitive capacities such as language, semantic memory, or verbal reasoning due to these cognitive processes’ distinctive characteristics.
More comments are on the page Evolutionary genetics and neuroscience included in the book Memory, language, and other brain abilities of the Global Cognitive Theory.
We would expect the contrary hypothesis regarding the inheritance of musical and artistic abilities –like with non-mathematical memory or intuition.
The problem with carrying out statistical analyses on these abilities’ evolutionary psychology is the lack of reliable data.
6.b) The Darwin-out experiment
The Darwin-out experiment is a proposed study (2011) on intelligence progress to verify the Conditional Evolution of Life -CEL- empirically.
The idea arose due to the remarkable adjustment of the September 2002 additional hypothesis of sexual selection regarding the initial April 2002 EDI Study, which implied a great sensibility of the evolutionary model of intelligence, even for groups of 10 individuals. Of course, it is always interesting to search for a more straightforward and definitive experiment.
To date, the new Darwin-out experiment is just a proposal, but it is possible thanks to the advances in biology and genetics. Moreover, the cost is not high, considering the implications involved.
The objective is to confirm The EDI Study’s results regarding women's security function in the sexual differentiation, the update of genetic information carried out by men, the hereditary nature of intelligence, and its 10% increment in each generation. The Darwin-out experiment's root is a linear discriminant analysis of the origin of the maternal X chromosome.
Repeating The EDI Study research on a large scale could revalidate it; however, a different experiment could corroborate it.
Following the conclusions outlined in the previous research and the CEL previsions, if we compare intelligence between individuals with and without updated chromosomes supporting intelligence, that is to say, with a generational gap, we should obtain higher IQ for the former ones.

An individual will always have an updated sexual chromosome, either X or Y, because it comes from the father. The other will not, as comes from the mother. The grandfather could have updated the maternal X chromosome in the previous generation (XGF); conversely, the grandmother did not update it (XGM). We were searching for this characteristic of a generational gap to discriminate between alternative evolutionary steps.
Due to the logic of optimization, intelligence would be mainly in the sex chromosomes. Anyway, the Darwin-out experiment would allow us to find the responsible ones.
The new Darwin-out experiment is exceptionally aseptic, as it does not incorporate per se any bias regarding intelligence evolution. What’s more, if there were significant biases in selecting the sample, it would not be a problem, as we will discuss.
The experiment consists of two stages.
Selection of a random sample
The first step would be to select a random sample of 100 women of a similar age, same race, and middle social stratum to reduce any possible biases, either genetic or environmental. Then, determine their IQ and the male or female source of the previous generation of the maternal X chromosome. In other words, if it comes from the maternal grandfather (XGF) or the maternal grandmother (XGM).
The sample should not have a significant bias. According to Darwin’s ideas and Mendel’s laws, approximately 50% of the maternal X chromosomes should come from the grandfather and the other 50% from the grandmother.
Of course, the larger the sample is, the better. The IQ test used will not influence the results from a gender perspective, whether balanced or not a priori. The selection is composed of solely one gender.
-
Hypothesis to verify
The hypothesis to verify is if the average IQ of the sample is above 100, then the proportion of XGF will be above 50%.
Menssalina experiment (2016) offers an exciting sample of 100 members of Mensa ** (an association of people with IQ over 98% of the population). It would make the verification more comfortable. According to The EDI Study outcomes (2002), the proportion of XGF could be 70% or higher. Furthermore, the Darwin-out experiment cost would be small, as the IQ tests would be redundant.
-
Another way to test the hypothesis is to rearrange the sample by their IQ.
Now, 50 women with lower IQ will have a lower proportion of XGF and higher XGM than the 50 women with higher IQ.
Darwin-out experiment Remove from biases with IQ rearrange sample 
Following the same reasoning, we could say that if we make four groups within the rearranged sample, the proportion of XGF should be more prominent, the higher the groups' IQ is.
Darwin-out experiment A positive correlation between XGF and IQ 
Another equivalent check is the CEL proposal on intelligence evolution or direct causality between more modern chromosomes and greater intelligence.
We divide the sample into two groups to verify it. One with XGM and the other with XGF, the first group's average IQ should be smaller than that of the second.
Darwin-out experiment Groups by the origin of X chromosome 
In this case, the number of people in each group does not necessarily have to be precisely half the sample number.
After having confirmed the hypothesis, the following extremes become evident.
The existence of evolution of intelligence in each generation
Realization of improvements in the genetic information exclusively by males
The elementary functions of intelligence are in the sex chromosomes X and Y or, at least, in one known chromosome.
The randomness of all genetic modifications and the theory of Darwin are incorrect.
The existence of a teleological intelligence different from the human one
The Darwin-out experiment with a sufficiently large sample and several groups could check The EDI Study’s coherence regarding the 10% of human intelligence evolution in each generation.
This empiric research will offer its results without biases, environmental interferences, technical intrusions, or the need for a precise definition of intelligence. Moreover, to understand this experiment, one does not need to have particular academic degrees or make a considerable effort.
A male sample would also do! Although perhaps it would have less sharpness in the results.
The male or mixed intelligence analysis would be identical, scheming the source of the only maternal X chromosome, from the grandfather or the grandmother.
The Darwin-out experiment's objective is not to deny or explain the possible differences between male and female intelligence but to scientifically strengthen the Conditional Evolution of Life.
When Darwin-out finished
the design of the experiment,
he happily went to tell Mª José.
‘I’m impressed,’ she told him,
‘And now what are you going to do?’
After thinking for a moment,
Darwin-out confessed,
‘I’m going to invite a friend of mine,
and I’m going to make her a Moon salad.’
To which Mª José asked,
‘Wow, cool! How is that done?’
‘It has some pretty little tomatoes and cucumber;
you cut a tomato into two pieces
and each one eats half’,
Darwin-out explained.
Then, Mª José exclaimed,
‘how romantic!’
