2.a) General properties of matter or Global Aether
Taking advantage of the fact that the general properties of matter can renormalize, we will try to connect them to make the assimilation of the new paradigm easier. As the new model grows in complexity, nuances will appear in the properties of matter. The following ideas offer a view of the structure and properties of matter renormalized several times over.
In addition to the many small renormalizations that Global Mechanics underwent during its initial development, it is useful to point out the switch from the previous semi-rigid model to Global Mechanics’ current elastic model. The change came after the review of the whole model because of the development of the Astrophysics and Cosmology book.
Although the new elastic model only adds the general property of matter concerning the constitution of Global Aether as unbreakable matter, this property significantly simplifies Global Mechanics by making the most complex mechanisms of the old semi-rigid model unnecessary.
On the previous page, we said the nature of the structure of matter is a three-dimensional net of unbreakable filaments that extend themselves along the whole universe. We call this 3D grid Global Aether.
Let us delve deeper into the characteristics or general properties of matter.
Three-dimensional structure
When one is wondering what gravity is, the first thing one thinks of is that it has to be a spatial structure, which can support the forces of gravity. Then, if we remove the radial symmetry of gravity, we will find that the three-dimensional structure with total symmetry is a general property of matter.
The images shown in this book refer to the three spatial dimensions of Euclidian geometry, and their goal is to get the brain accustomed to the real existence and the characteristics of Global Aether as a state of matter, which configures gravity in the ordinary world known by all of us. The concept is essential to follow the explanations of the new physics model’s properties and nature, and consider that the existence of other worlds and time travel is science fiction.
The proposed three-dimensional structure of matter will be composed of filaments that form a 3D grid of reticules.
Structure of matter Reticule of Global Aether 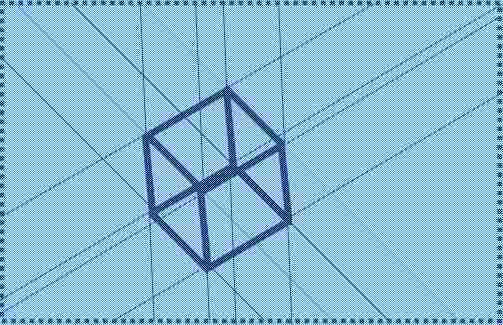
-
Reticules with a cube shape
The crossing of the Global Aether filaments forms cubes.
The shape of a cube is the simplest for the brain to visualize. Any other geometric figure could also be possible, provided it does not forbid the physical state with the general property of matter of theoretical, total symmetry in the absence of forces of gravity or electromagnetism.
Unbreakable filaments
This characteristic or property of matter justifies the principle of conservation of matter (understanding matter as in the Global Mechanics sense).
Continuous nature of matter
Likewise, the nature of the unbreakable filaments makes matter continuous in the entire universe; in other words, the Global Aether particle extends itself throughout the whole universe. After almost 2500 years of a discontinuous nature of matter, who would have thought it? We hope Democritus would not mind!
-
The matter is formed exclusively by the filaments´ matter
The space between filaments is empty and hollow in the ideal state of total symmetry.
This characteristic of matter will be advantageous to us when developing the theory of the formation of mass and the new theory of the atom.
Elasticity
This property of matter is very intuitive, but we have to consider that it also has a colossal rigidity at the scale at which we operate.
The elasticity explains the principle of energy conservation as it is an energy of reversible deformation. Perfect elasticity is an essential requirement for the principle of energy conservation.
The concept of elastic energy is more difficult than it appears at first. An elastic object needs internal elements with elastic properties and so on. On another hand, elastic energy needs elements in constant motion or vibration, as a full static element would not have any internal energy.
In short, the property of elasticity configures the Global Aether as a real net in constant vibration or resonance.
Longitudinal elasticity, bi-dimensional or longitudinal curvature elasticity and transversal elasticity, together with the unbreakable nature of matter’s filaments, support the Principle of Global Conservation, which covers the law of conservation of matter and the law of conservation of energy.
Longitudinal elasticity
This quantitative characteristic has its relevance; the elasticity of the filaments could make them reach a length of ten, a hundred or a thousand times longer than their length in the absence of traction forces. For now, we have the liberty to fix this parameter; nevertheless, the size of the stable elementary particles with mass –protons and neutrons– could help us to delimit this general property of matter quantitatively.
One should not confuse the expansion or contraction of Global Aether with variations of space itself, as some physics theories do.
Bi-dimensional or longitudinal curvature elasticity
The result of the forces derived from the elastic tension of the longitudinal curvature of the filaments in Global Aether will be responsible for the atractis causa of the gravitational theory in Global Mechanics.
Transverse elasticity
The elasticity of a transverse nature is a general property of matter, which will be the concrete base of the electromagnetic interaction.
This general property of matter will relate, together with the property of longitudinal elasticity and longitudinal curvature elasticity, with the weak and strong nuclear interactions and with the formation of mass.
The general properties of matter try to describe the nature of Global Aether from both an internal and an external point of view. The elastic properties of Global Aether imply that within its constitution it has smaller elements. Perhaps the limit of transverse or longitudinal elasticity links to the size of the reticule.
In short, the filaments configure themselves as the mechanism for the transmission of the minimum unit of energy, unavoidably related to the Planck constant –though it is most probably not as constant as it appears to be.
On the following pages, we will analyze the composition, characteristics, and properties of matter in general for each of the big categories of the 3D reticular structure of matter.
